Haryana State came into existence on 1st November, 1966 and the Punjab Gram Panchayat Act, 1952 was made applicable to the PRIs in Haryana. Pursuant to the 73rd Constitutional amendment in 1992, the Haryana Panchayati Raj Act, 1994 was framed which came into force w.e.f. April 22, 1994.
Thereafter Haryana Panchayati Raj Election Rules, 1994 were formulated on 24th August, 1994 followed by Haryana Panchayati Rules, 1995, notified on 16th February1995. Subsequently the Haryana Panchayati Raj Finance Budget/ Accounts/ Audit/ Taxation and works rules 1996 were also notified on 14th August, 1996.
Under the Haryana Panchayati Raj Act 1994, the Panchayati Raj Institutions have been entrusted with duties & functions related to all the 29 subjects listed in Eleventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Administrative Division of Haryana
| Divisions | 6 |
| Districts | 22 |
| Blocks | 142 |
| Zila Parishads | 21 |
| Panchayat Samitis | 126 |
| Gram Panchayats | 6225 |
| No. of Villages | 7422 |
Relevant Statistics
The position of elected representatives of three tiers along with representation of women, SC and BC based on elections held in 2016 is as under
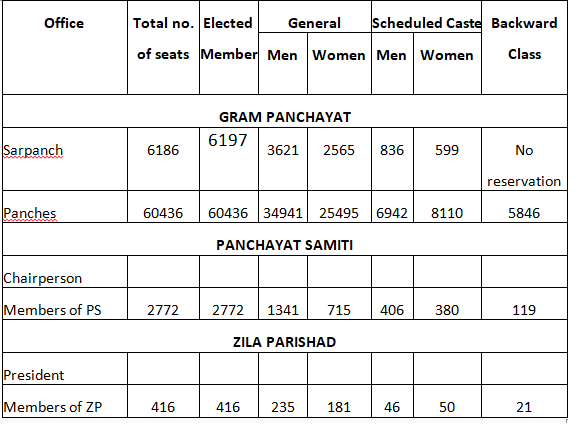
Category wise distribution of Sarpanch in Haryana
| Total | SC | Woman | BC | |
| Sarpanch | 6186 | 1436 | 2565 | – |
| Panches | 60436 | 15467 | 25495 | 5846 |
| Zila Parishad | 374 | 82 | 132 | 21 |
| Panchayat Samitis | 2772 | 697 | 956 | 119 |
Districtwise Total Number of Gram Panchayats in Haryana
| Sr. No. | Name of District | No. of Panchayats |
| 1. | Ambala | 400 |
| 2. | Bhiwani | 312 |
| 3. | Charkhi Dadri | 167 |
| 4. | Faridabad | 100 |
| 5. | Fatehabad | 259 |
| 6. | Gurgaon | 166 |
| 7. | Hisar | 300 |
| 8. | Jind | 247 |
| 9. | Jhajjar | 300 |
| 10. | Kaithal | 277 |
| 11. | Karnal | 395 |
| 12. | Kurukshetra | 404 |
| 13. | Mahendergarh | 343 |
| 14. | Mewat (Nuh) | 325 |
| 15. | Palwal | 263 |
| 16. | Panchkula | 135 |
| 17. | Panipat | 178 |
| 18. | Rewari | 365 |
| 19. | Rohtak | 142 |
| 20. | Sonipat | 341 |
| 21. | Sirsa | 318 |
| 22. | Yamuna Nagar | 490 |
| Total | 6227 |
History of Panchayati Raj in the Haryana State
After Independence with the enactment on the Punjab gram panchayat Act 1952 gram panchayats were set up at the village level on a mandatory basis. This ad was later amended in 1960 and when it became an independent state in 1966 the local governments institutions operating in the stale had three tiers.
These included the gram panchayats panchayat samitis and Zilla parotids formed under the 1961 Punjab panchayat Samitis and Zilla parishads Act. Till 1973 the three-tier structure inherited from Punjab were maintained in Haryana, In 1972 an adhoc committee was constituted to evaluate- the performance of the Zilla parishads which expressed the view that the Zilla parishads be abolished as they were superfluous bodies which had failed to perform their coordinating functions. As a result the Zilla parishads were abolished from 13th July 1973.However the real motive behind this move was believed to be political as the political leadership did not want to share powers with the Panchayati Raj leadership.
The gram sabha which had become almost inactive prior to 1966 was crippled further. The authority of the gram panchayats was also eroded as un authorised possession of village common lands by politically affluent persons enjoyed the support of the bureaucracy adversely affected the gram panchayats. Government grants to these bodies were also drastically reduced.
The authority of the Sarpanch was also undermined by making provisions for indirect elections to the post. Control over the funds of gram panchayats were transferred to the gram sachiv. However on 22nd April 1994 in conformity with the 73rd amendment 1992 the Haryana Panchayati raj Act 1994 came into force restoring the three tier structure and gram sabha in Conformity with the act prevailing all over the country (R Singh 1994)
